In May 2017, you bought and placed in service a car costing $31,500. You did not what is a depreciable asset elect a section 179 deduction and elected not to claim any special depreciation allowance for the 5-year property. You used the car exclusively for business during the recovery period (2017 through 2022).
Which assets can be depreciated?
Regardless of the method of depreciation employed, the depreciable property must have the same cost basis, useful life, and salvage value upon the end of its useful life. In some cases, businesses can choose to capitalize an asset, taking an expense (write off) in the current tax period and forgoing future depreciation, thus rendering it a non-depreciable asset, following IRC section 179 rules. Depreciable assets include all tangible fixed assets of a business that can be seen and touched such as buildings, machinery, vehicles, and equipment. Carrying value is the net of the asset account and the accumulated depreciation. Salvage value is the carrying value that remains on the balance sheet after which all depreciation is accounted for until the asset is disposed of or sold.
- The use of property must be required for you to perform your duties properly.
- The expense amounts can then be used as a tax deduction, reducing the tax liability of the business.
- For example, a purchase classified as a vehicle might be depreciated over five years, while a purchase classified as furniture might instead be depreciated over seven years.
- The depreciation rate is used to calculate an asset’s annual depreciation, and then all accumulated depreciation from the first year of use until the last year of usage is added.
Table of contents:
For a description of related persons, see Related persons in the discussion on property owned or used in 1986 under What Method Can You Use To Depreciate Your Property? For this purpose, however, treat as related persons only the relationships listed in items balance sheet (1) through (10) of that discussion and substitute “50%” for “10%” each place it appears. Other property used for transportation includes trucks, buses, boats, airplanes, motorcycles, and any other vehicles used to transport persons or goods. In May 2023, Sankofa sells its entire manufacturing plant in New Jersey to an unrelated person.
Depreciation of Long-Term Assets
![]()
Physical goods such as old cars that can be sold for scrap and outdated buildings that can still be occupied may have residual value. More depreciation expense is recognized earlier in an asset’s useful life when a company accelerates it. Almost all intangible assets are amortized over their useful life using the straight-line method.

When using the straight line method, you apply a different depreciation rate each year to the adjusted basis of your property. You must use the applicable convention in the year you place the property in service and the year you dispose of the property. On July 2, 2021, you purchased and placed in service residential rental property.
- You start by combining all the digits of the expected life of the asset.
- With a book value of $73,000, there is now only $56,000 left to depreciate over seven years, or $8,000 per year.
- You multiply the reduced adjusted basis ($58) by 100% to arrive at the depreciation deduction for the sixth year ($58).
- Both options spread the cost of an asset over its useful life and a company doesn’t gain any financial advantage through one rather than the other.
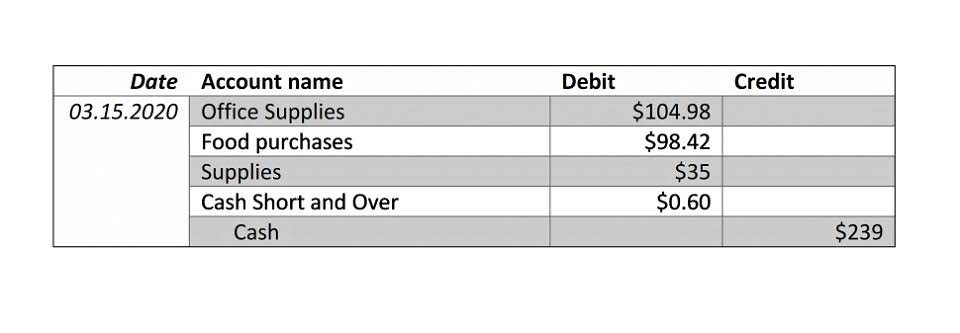
Accumulated Depreciation, Carrying Value, and Salvage Value
If you are married, how you figure your section 179 deduction depends on whether you file jointly or separately. If you file a joint return, you and your spouse are treated as one taxpayer in determining any reduction to the dollar limit, regardless of which of you purchased the property or placed it in service. If you and your spouse file separate returns, you are treated as one taxpayer for the dollar limit, including the reduction for costs over $2,890,000. You must allocate the dollar limit (after any reduction) between you equally, unless you both elect a different allocation. If the percentages elected by each of you do not total 100%, 50% will be allocated to each of you. You can include participations and residuals in the adjusted basis of the property for purposes of computing your depreciation deduction under the income forecast method.

Get Your Questions Answered and Book a Free Call if Necessary
Both of these can make the company appear “better” with larger earnings and a stronger balance sheet. The difference between the end-of-year PP&E and the end-of-year accumulated depreciation is $2.4 million, which is the total book value of those assets. Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
Submit Your Info Below and Someone Will Get Back to You Shortly.
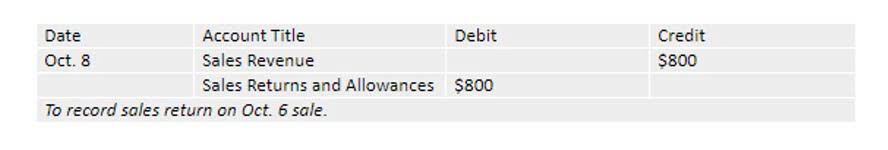
You can file an amended return to correct the amount of depreciation claimed for any property in any of the following situations. You repair a small section on one corner of the roof of a rental house. However, if you completely replace the roof, the new roof is an improvement because it is a restoration of the building.
